Research
Advanced Medical Research Center
Advanced Medical Research Center(SENTANKEN)conducts basic studies aimed at overcoming cancer and lifestyle diseases and translational researches which applies the scientific finding to clinical medicine. It has three omics centers – genomics, proteomics, cellomics –and a biobank, collaborates within YCU and with other research institutions, and promote translational researches. AMRC is also involved in a number of R&D, working with the industry. Our goal is to make our research findings available to the society without delay.
Outline, Structure & Function of the Advanced Medical Research Center >
Outline, Structure & Function of the Advanced Medical Research Center >

RESEARCH > ADVANCED MEDICAL RESEARCH CENTER
Message from the Director
The Advanced Medical Research Center (SENTANKEN) of Yokohama City University(YCU) was established in 2006. The assignment of SENTANKEN is to facilitate advanced medical research associated with diseases such as cancer and lifestyle-related diseases. SENTANKEN is focused on basic researches in the field of genomics, proteomics and cellomics, as well as translational researches, which can fill the gap between basic and clinical researches, and promotes not only intramural collaboration but also between government, industry and academia.
Our goal is to make an attractive YCU that can contribute to the community by delivering the research outcomes of our basic and clinical researches promptly to the citizens of Yokohama and by connecting these activities for the revitalization of industries in Yokohama.
Our goal is to make an attractive YCU that can contribute to the community by delivering the research outcomes of our basic and clinical researches promptly to the citizens of Yokohama and by connecting these activities for the revitalization of industries in Yokohama.

Professor Yukie Yamaguchi
Director, Advanced Medical Research Center
Research News
2024-11-05
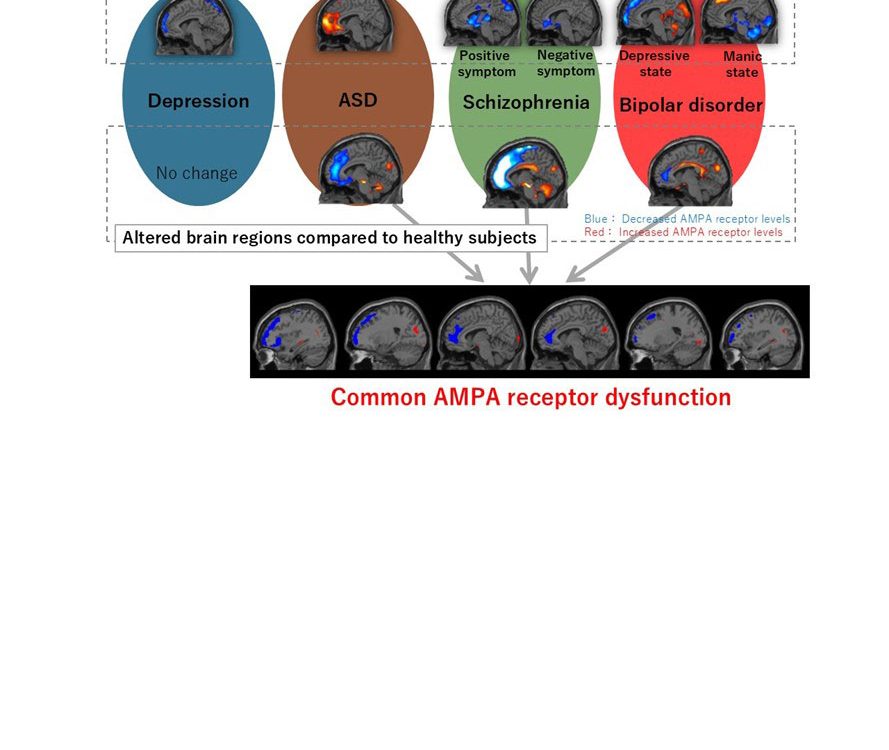
Researchers employ an innovative method to visualize an essential molecule for neurotransmission in patients with various psychiatric diseases

Contact info
sentan@yokohama-cu.ac.jp