情報解析
Meta analysis

新生突然変異の大規模なメタ解析
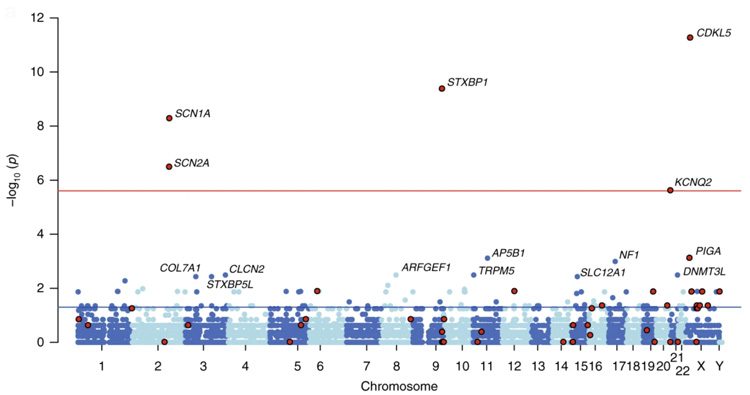
単一遺伝子疾患の一部は特定の遺伝子における新生突然変異が原因です。この突然変異は、患者とその両親の三人のDNAサンプルを全エクソーム解析することで同定することが出来ます。この突然変異が多く見られる遺伝子を各疾患において統計的に探索することで、その疾患の原因遺伝子を同定することが出来ます。
我々は、これまでの研究で単一遺伝子疾患をもつ9000以上の家系において突然変異を同定してきました。特に知的障害や自閉症スペクトラム障害などを含む神経発達症群(Neurodevelopmental disorders)については、1000以上の家系を解析しています。これらの神経発達症群を持つ家系において、上記の方法を用いることで、多くの新規の原因遺伝子を同定することに成功しています(図)。今後さらに家系を集積し、既報研究で報告された家系も含めた数万家系において、神経発達症群の新規の原因遺伝子の大規模な同定を試みる予定です。
Large-scale meta-analysis of de novo mutations
Some genetic diseases are caused by de novo variants at some protein-coding genes. The de novo variants are detected with whole-exome sequencing of an individual and his/her parents. Statistically testing gene-specific enrichment of de novo variants in indviduals with a disease, we can identify novel causative genes of the disease.
We have performed whole-exome sequencing of more than 9000 families of genetic diseases. Especially, we have analyzed more than 1000 families of neurodevelopmental disorders and identified many causative genes using the above-mentioned method. We will detect de novo variants in more families, analyze them with those reported by other laboratories, and identify novel causative genes of neurodevelopmental disorders on a large scale.





