EF-hand proteins
EF-hand proteins are homologous; they have all evolved from a
common
precursor. They contain from two to twelve copies of the EF-hand
domain. The
EF-hand is about thirty amino acids long and consists of an alpha-helix
(E), loop, and second alpha-helix (F). Usually a Ca
2+
ion is bound in the
loop under physiological conditions; however, 30% of all known
EF-hands do not bind calcium. With only a few exceptions all EF-hand
containing proteins
are found in the cytosols of eukaryotic cells. Most of them function
as transducers of infor mation. In so called quiescent cells the
concentration of the free Ca
2+ ion is about 10
-7.2
M;
following a stimulus to the cell [Ca
2+] rises to
~ 10
-5.8 M. Many
EF-hand proteins are calcium modulated. In a quiescent cell they are
in the apo or in the magnesium form; following stimulation they are in
the calcium form. These calcium signals are tuned by complex spatial
and temporal distributions, as well as by differing affinities and
binding rates of calcium modulated proteins. We summarize the
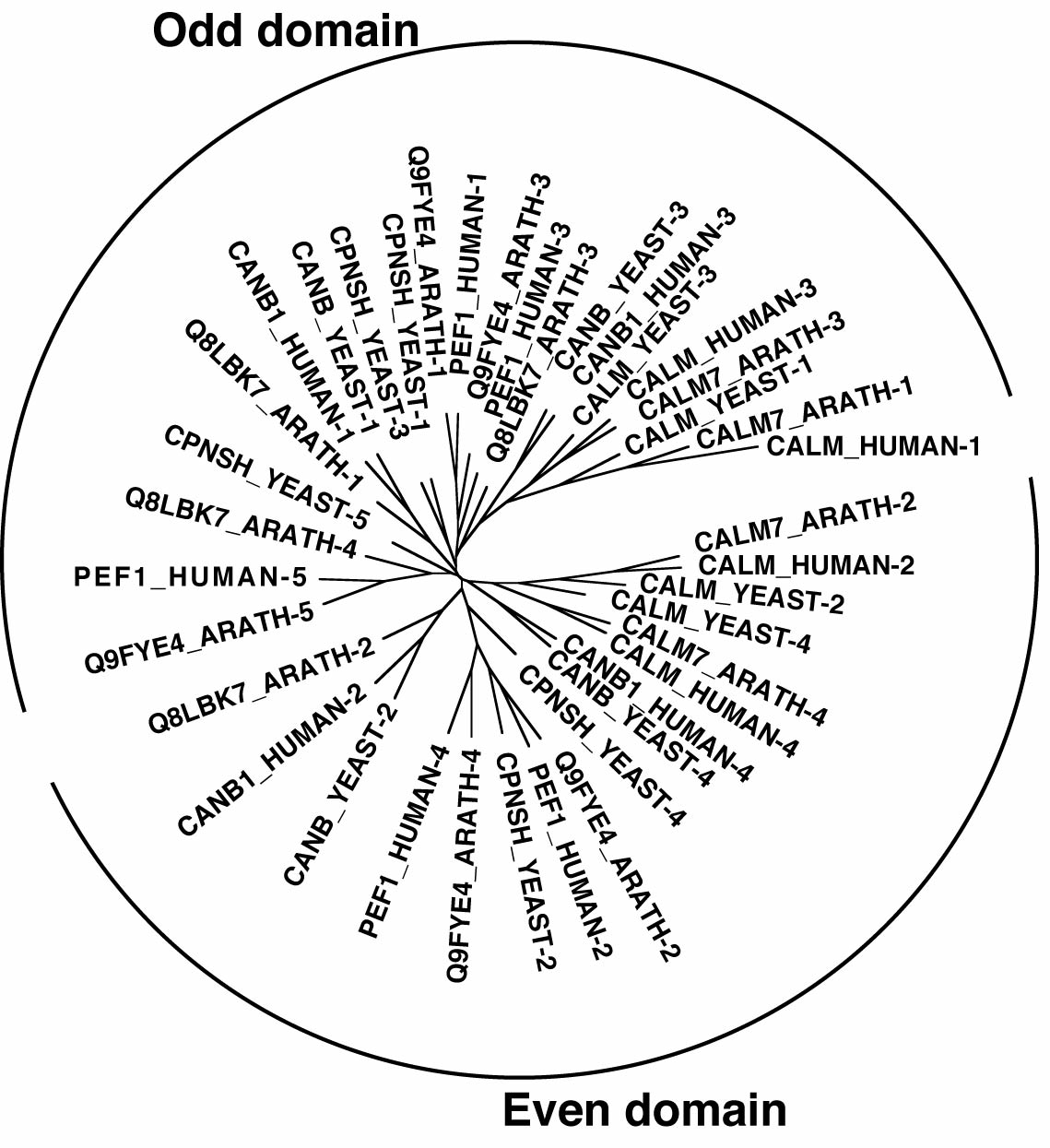
characteristics of the 66 known subfamilies of
EF-hand proteins in old Database and 156 subfamilies of EF-hand proteins in the updated Database.
Contents
-
Characteristics of
EF-hands and of EF-hand Proteins
- Functions
of EF-hand Proteins
- EF-hands
and Ca2+ Binding
- Pairs
of
EF-hands
- Congruence
within and among EF-hand Subfamilies
- Subfamilies of
EF-hand
Proteins (Old EF-hand Database)
- Calssifications of subfamilies (Updated EF-hand protein Database, 2016)
- Perspectives
-
References
EF-hand Database
Hiroshi Kawasaki
Graduate School of Medical Life Science,
Yokohama City University,
Suehiro-cho 1-7-29, Tsurumi-ku, Yokohama 230-0045, Japan
kawasaki@yokohama-cu.ac.jp
Robert H. Kretsinger
Department of Biology, University of Virginia,
Charlottesville, VA,
22901, USA
rhk5i@virginia.edu
 EF-hand calcium binding proteins
EF-hand calcium binding proteins